Every process has an environment block that contains a set of environment variables and their values. There are two types of environment variables: user environment variables (set for each user) and system environment variables (set for everyone). An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer.
By default, a child process inherits the environment variables of its parent process. Programs started by the command processor inherit the command processor’s environment variables.
How to set or change the Environment Variables?
Windows
Windows 10 and Windows 8
- In Search, search for and then select: System (Control Panel)
- Click the Advanced system settings link.
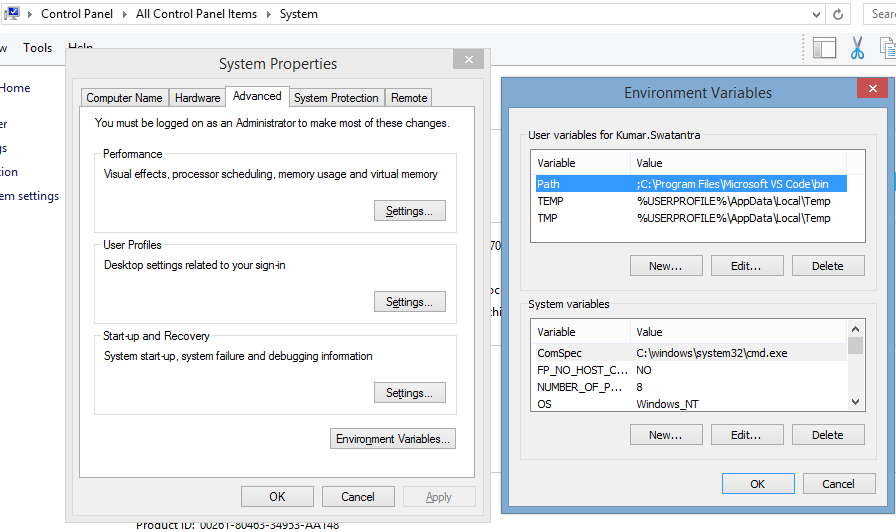
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the
PATHenvironment variable and select it. Click Edit. If thePATHenvironment variable does not exist, clickNew. - In the Edit System Variable (or New System Variable) window, specify the value of the
PATHenvironment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK. - Reopen Command prompt window, and run your java code.
Windows 7
- From the desktop, right click the Computer icon.
- Choose Properties from the context menu.
- Click the Advanced system settings link.
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the
PATHenvironment variable and select it. Click Edit. If thePATHenvironment variable does not exist, clickNew. - In the Edit System Variable (or New System Variable) window, specify the value of the
PATHenvironment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK. - Reopen Command prompt window, and run your java code.
Windows Vista
- From the desktop, right click the My Computer icon.
- Choose Properties from the context menu.
- Click the Advanced tab (Advanced system settings link in Vista).
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the
PATHenvironment variable and select it. Click Edit. If thePATHenvironment variable does not exist, clickNew. - In the Edit System Variable (or New System Variable) window, specify the value of the
PATHenvironment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK. - Reopen Command prompt window, and run your java code.
Windows XP
- Select Start, select Control Panel. double click System, and select the Advanced tab.
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the
PATHenvironment variable and select it. Click Edit. If thePATHenvironment variable does not exist, clickNew. - In the Edit System Variable (or New System Variable) window, specify the value of the
PATHenvironment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK. - Reopen Command prompt window, and run your java code.
Mac OS X
To run a different version of Java, either specify the full path, or use the java_home tool:
% /usr/libexec/java_home -v 1.8.0_73 --exec javac -version
Solaris and Linux
- To find out if the path is properly set:
In a terminal windows, enter:
% java -version
This will print the version of thejavatool, if it can find it. If the version is old or you get the error java: Command not found, then the path is not properly set. - Determine which java executable is the first one found in your PATH
In a terminal window, enter:
% which java
Set the PATH permanently
To set the path permanently, set the path in your startup file.
Note: Instructions for two most popular Shells on Linux and Solaris are listed.
Bash Shell
Edit the startup file (~/.bashrc)
- Modify PATH variable
PATH=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0/bin:$PATH
export PATH - Save and close the file
- Load the startup file
% . /.profile - Verify that the path is set by repeating the
javacommand
% java -version
C Shell (csh)
Edit the startup file (~/.cshrc)
- Set Path
set path=(/usr/local/jdk1.8.0/bin $path) - Save and close the file
- Load the startup file
% source ~/.cshrc - Verify that the path is set by repeating the
javacommand
% java -version